Call Us Today 817-737-7668
Peri-implantitis is a progressive inflammatory condition affecting tissues around dental implants. It can cause gum inflammation, bone loss, and implant instability if untreated. With dental implants becoming more popular, peri-implant diseases are also rising.
Early detection and timely intervention are crucial to prevent severe complications. Traditional treatments often fall short of completely removing harmful biofilm and promoting tissue regeneration.
However, modern strategies now offer more effective solutions. This blog explores peri-implantitis, its causes, symptoms, and smarter treatment approaches. It will also discuss preventive strategies to maintain healthy implants for the long term.
What Is Peri-Implantitis?
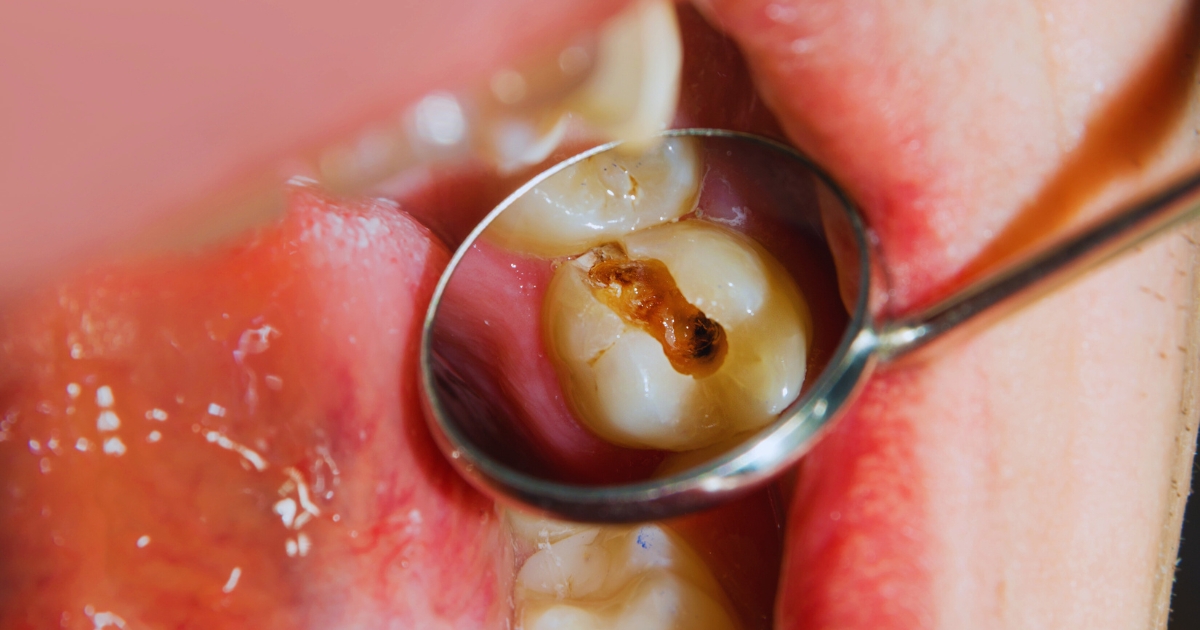
Peri-implantitis is a bacterial infection around dental implants, causing inflammation and bone loss. It is one of the most common peri-implant diseases, which can compromise implant stability. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, and existing gum disease are major risk factors. Inadequate implant placement and improper prosthetic design can also contribute to the condition.
The primary symptom of peri-implantitis is gum inflammation, which may include redness, swelling, and bleeding. Other symptoms include pus discharge, implant mobility, and bad breath. Left untreated, it leads to progressive bone loss, potentially resulting in implant failure.
The biological process begins with bacterial biofilm accumulation around the implant surface. This triggers an inflammatory response as the body tries to fight the infection. Over time, chronic inflammation damages surrounding bone and soft tissues. The infection progresses if the biofilm remains despite regular oral care. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to control infection and prevent complications.
The Smarter Way: Modern Strategies and Innovations
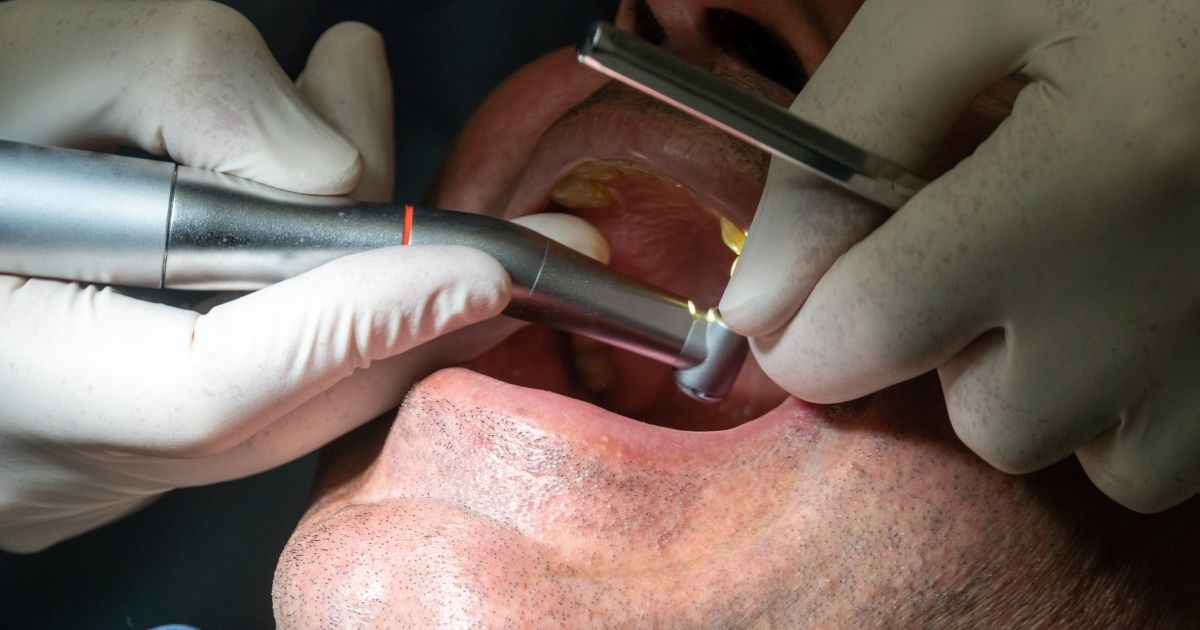
Traditional methods like mechanical debridement and antibiotics have limitations in treating peri-implantitis. Fortunately, modern strategies now provide more predictable outcomes.
1. Guided Biofilm Therapy (GBT)
GBT uses airflow devices with a specialized powder to remove biofilm, plaque, and stains. It targets hard-to-reach areas without damaging implant surfaces. This method ensures thorough cleaning and supports healthier peri-implant tissues. Research shows GBT improves long-term implant success when combined with regular maintenance.
2. Laser-Assisted Therapy
Laser technology has revolutionized peri-implantitis treatment by precisely removing infected tissue. It disinfects the implant surface and promotes faster tissue healing. Lasers reduce bacterial load without causing thermal damage. Additionally, this non-invasive approach minimizes discomfort and shortens recovery time.
3. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy (aPDT)
aPDT involves applying a light-sensitive agent to infected tissues, followed by light activation. This process generates reactive oxygen species, killing bacteria without harming healthy cells. aPDT is an effective adjunct to mechanical cleaning and enhances antibacterial effects in persistent infections.
4. Regenerative Techniques
Peri-implantitis often causes significant bone loss, requiring advanced regenerative techniques. Bone graft materials combined with growth factors stimulate new bone formation. Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) techniques create a framework for bone and soft tissue healing. These approaches help restore implant stability and improve long-term success.
By combining these advanced techniques, clinicians can effectively manage peri-implant diseases Alliance and improve outcomes.
Preventive Strategies: The Best Long-Term Approach
Prevention plays a key role in managing peri-implantitis and other peri-implant diseases. A proactive approach helps maintain implant health and reduces treatment needs.
1. Regular Professional Monitoring and Maintenance
Routine dental check-ups are essential for monitoring peri-implant tissues. Dentists use specialized tools to assess gum health and detect early inflammation. Regular professional cleanings help prevent biofilm accumulation, reducing the risk of peri-implantitis.
2. Patient Education on Oral Hygiene Practices
Educating patients about proper oral hygiene is critical. Patients must brush their teeth and implants twice daily using soft-bristled brushes. Interdental brushes or water flossers help clean around implant surfaces. Dentists should also emphasize the importance of antibacterial mouthwashes to reduce bacterial load.
3. Innovations in Implant Design
Modern implant designs now incorporate surface treatments that minimize bacterial adhesion. Implants with micro-roughened surfaces promote better osseointegration while discouraging biofilm formation. Additionally, improved prosthetic connections reduce micro-gaps where bacteria can accumulate. These innovations enhance implant longevity and lower peri-implant disease risks.
Preventive care, combined with modern technology, ensures better outcomes for implant patients.
Peri-implantitis is a serious condition that can jeopardize implant success if ignored. Modern treatment methods like GBT, laser therapy, aPDT, and regenerative techniques offer effective solutions. Early diagnosis and timely intervention are crucial to prevent further complications. Patients should prioritize oral hygiene and attend regular dental check-ups.
If you notice any signs of inflammation or implant discomfort, consult our dental professionals immediately. Protect your dental implants with smart, evidence-based approaches today.