Call Us Today 817-737-7668
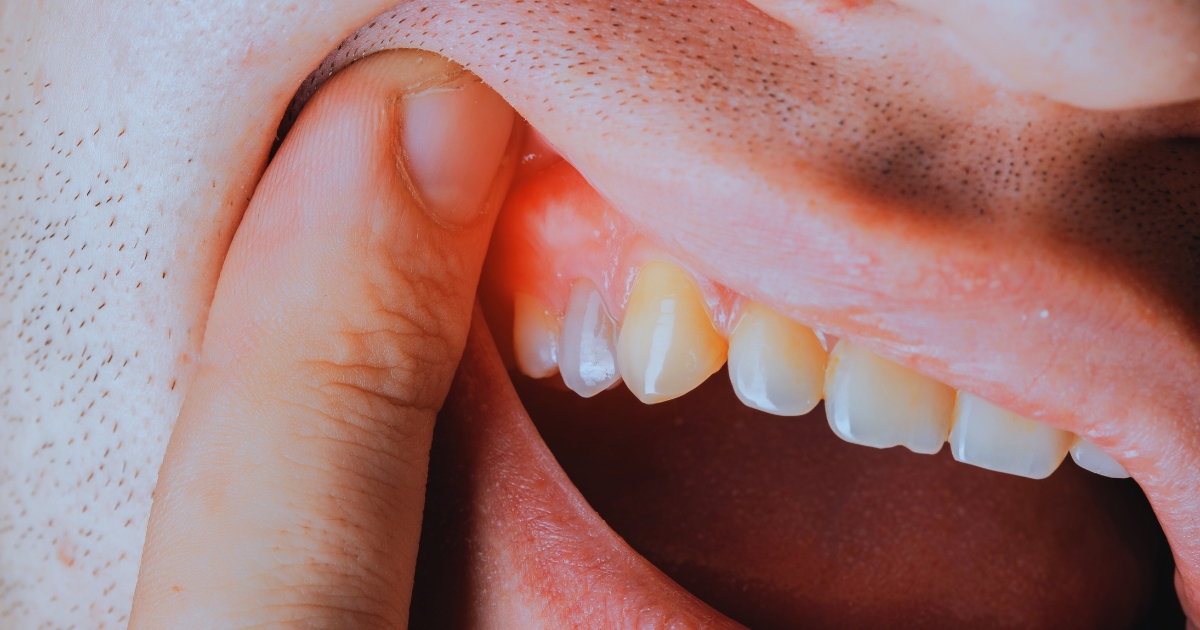
You brush twice daily and floss daily, yet your gums appear to be receding. This is shocking, right? Most adults aren’t aware of gingival recession until sensitivity sets in or teeth appear longer. It creeps up silently, imperceptibly, and usually without pain.
However, the catch is that it’s prevalent than you might imagine. If you deny it, it does more harm than good.
What is Gingival Recession?
Gingival recession takes place when gum tissue recedes and reveals tooth roots. Recession of gums reveals sensitive areas of your teeth. Healthy gums fit snugly around teeth and provide protection and stability. Receded gums create gaps for bacteria to accumulate. That accumulation can cause additional harm and pain.
You might feel tooth sensitivity or observe longer teeth. These are primary indicators of gingival recession. Early detection significantly prevents irreversible damage.
Why Does It Happen in Adults?
Aging makes gingival recession more likely because of wear over time and thinning gums. Poor oral hygiene leads to plaque that results in gums becoming inflamed and receding.
Overaggressive tooth brushing will erode gum tissue. Gradually, it causes gingival recession. Periodontal disease, known as “the silent dentist,” destroys tooth-supporting structures.
Genetics is also involved. You may be susceptible to thinner gums. In addition, smokers risk more because of limited blood supply to gums. Grinding and malalignment load gums and cause them to recede.
All adults need to know gingival recession helps to improve oral health if detected early. Prevention significantly avoids more extensive problems.
How Does It Progress?
Gingival recession begins gradually—perhaps a tiny sensitivity in teeth or an elongated-looking tooth. In early stages, one may not even notice. As it progresses, spaces develop between tooth and gum.
These spaces harbor bacteria and food and cause inflammation. If you leave them untreated, gingival recession increases and causes root exposure, toothache, and bone loss. Teeth eventually loosen because they lose support.
Don’t let it go that far. Treating it at an early stage ensures that gingival recession contributes to better oral health before damage turns permanent.
Assessing Severity
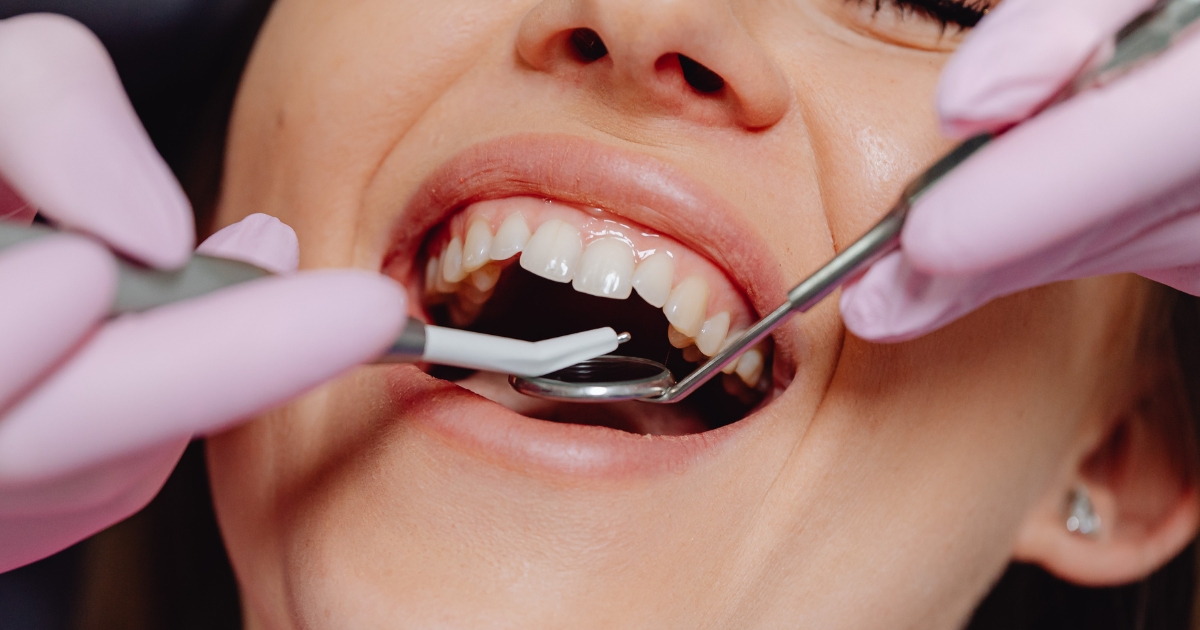
Dentists measure this issue with instruments such as Miller’s classification system. This procedure helps identify how far the gums have receded.
Class I is mild and has no bone loss. On the other hand, Class II has moderate gum loss with no bone exposure. Class III and IV entail severe tissue and bone loss.
It is to be stated that every stage requires particular attention. Minors can be treated with just lifestyle changes. Contrary to this, serious ones need surgery.
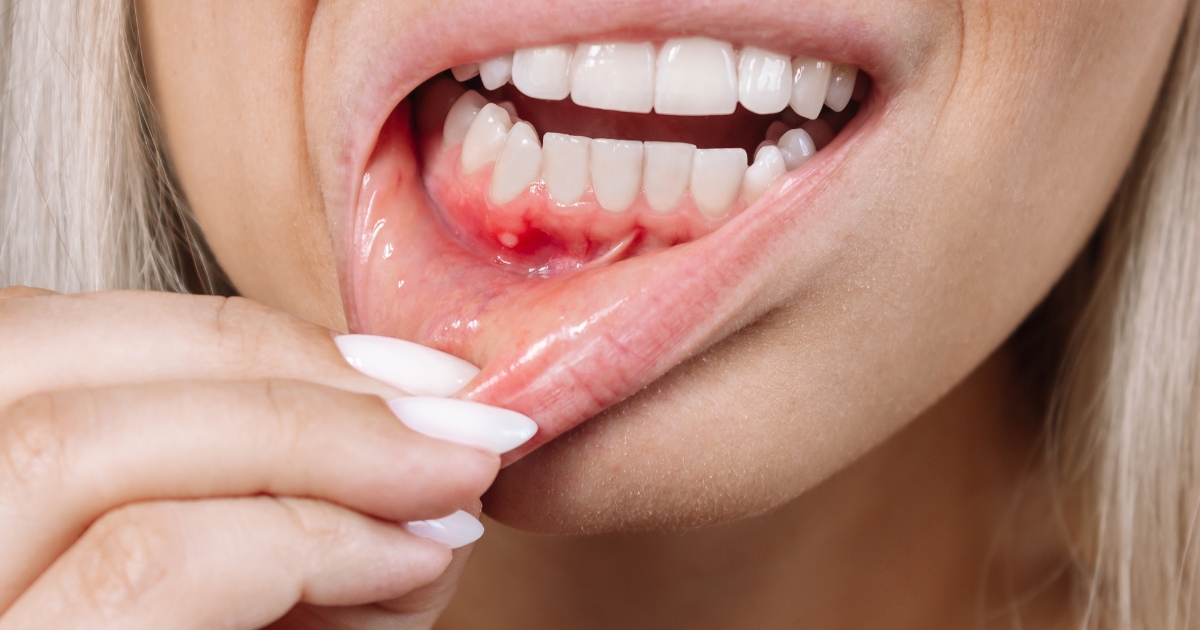
When your gums are bleeding, are sensitive, or teeth appear longer—see a dentist. Early action guarantees gingival recession leads to improved oral health and prevents long-term problems.
Treatment Options
A mild one is successfully treated with non-surgical measures such as desensitizing toothpaste and composite bonding. Soft-bristled toothbrushes and improved brushing also alleviate the condition.
Severe instances require surgery like gum grafting or guided tissue regeneration. These restore lost tissue and toughen your gumline.
Consider regular cleanings and exams to prevent more recession. In addition, quitting tobacco and grinding treatment also have benefits. Preventive care is critical. Early treatment ensures that this dental problem works to make oral health better in the long run and keeps your smile strong and confident.
Gingival Recession is common in adults. However, early action makes all the difference. Watch for subtle signs and act fast. Regular dental visits, proper hygiene, and lifestyle changes go a long way.
Remember, gingival recession contributes to better oral health if you treat it early. Don’t wait for pain to take action—prevention and awareness protect your smile for life.